Markup Language
A Markup language define the rules that help to add meaning to the content and structure of documents
They are classified as
-
Stylistic Markup – It determines the presentation of the document
-
Structure Markup – It defines the structure of the document
-
Semantic Markup – It determines the contents of the document
 |
Tools Used for Manual Markup
 |
Drawbacks of HTML
- HTML is the most famous markup language derived from SGML
-
It was created to mark up technical papers so that they could be transferred across different platforms for the scientific community
-
It is now used by non scientific users also, who are concerned about the presentation of their document
-
Fixed tag set
-
Presentation technology does not relate to the contents
-
It is flat language, no programming construct
-
HTML is not international
-
Data interchange is impossible
-
Does not have a robust linking mechanism
-
HTML is not reusable
SGML
- The system of formatting documents was named as Generalized Markup Language (GML)
-
The GML was fine tuned and it came to be known as Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML)
-
SGML is considered to be the mother of all markup language
-
In 1969, Charles Goldfarb was leading an IBM research project on integrated law office information systems. Together with Edward Mosher and Raymond Lorie he invented the Generalized Markup Language (GML) as a means of allowing the text editing, formatting, and information retrieval subsystems to share documents.
Features of SGML
- It describes markup language, allowing authors to create their own tags that relate to their content
-
It needs a file that would contain all the rules for the language, for its interpretation
-
The Markup language derived from SGML are called as SGML application
HTML and XML code Examples
<UL>
<LI> JAMES BOND
<UL>
<LI> CLIENT ID : 100
<LI> COMPANY : XYZ Corp.
<LI> Email : james@usa.net
<LI> Phone : 3336767
<LI> Street Adress : 25th St.
<LI> City : Toronto
<LI> State : Toronto
<LI> Zip : 20056
</UL>
</UL>
<Details>
<CONTACT>
<PERSON_NAME>James Bond</PERSON_NAME>
<ID> 100 </ID>
<COMPANY> XYZ Corp. </COMPANY>
<Email> james@usa.net</Email>
<Phone> 3336767 </Phone>
<Street> 25th St. </Street>
<City> Toronto </City>
<State> Toronto </State>
<ZIP> 20056 </ZIP>
</CONTACT>
</Details>
About XML
- XML stands for Extensible Markup Language (XML)
-
It overcomes all the drawbacks of HTML
-
It allows the user to define their own set of tags and also makes it possible for the others to understand it
-
It is very much flexible than HTML
-
It inherits the features from SGML and combines it with the features of HTML
-
It is a smaller version of SGML
-
XML document does not DO anything. It is just pure information wrapped in tags. Someone must write a piece of software to send, receive or display it.
Features of XML
- XML is a metalanguage and it describes other languages
-
The data contained in the XML file could be displayed in different ways
-
It could also be offered to other applications for further processing
-
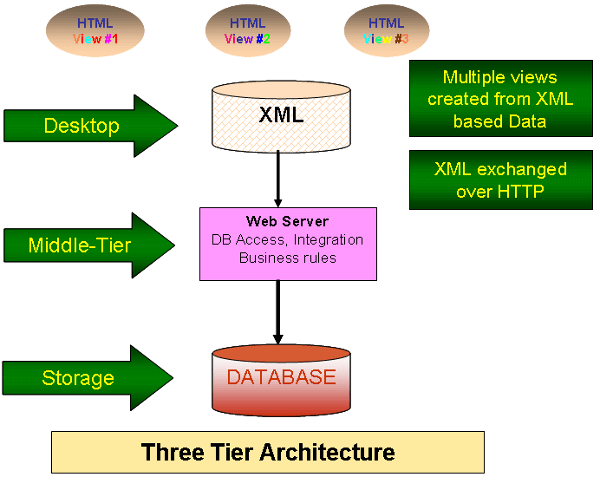
Style sheets help transforming structured data into different HTML views to display data on different browsers. [ XSLT ]


Benefits of XML
Business Benefits
- Information Sharing : Explain that it is possible to define data formats in XML and build tools using XML, which will read, write and transform data between XML and other formats.
-
Single application usage : For an application it is not necessary that the entire application be coded using XML. However, some specific parts of an application that involve formatting the data or transferring the data between applications may be coded with the help of XML.
-
Content Delivery : XML has the ability to support different users and channels, and to build more efficient applications. Channels include the information delivery mechanisms such as digital TV, phone, the Web, and multimedia/touchscreen kiosks.
Technological benefits
-
Re-use of data
-
Separation of data and presentation
-
Extensibility
-
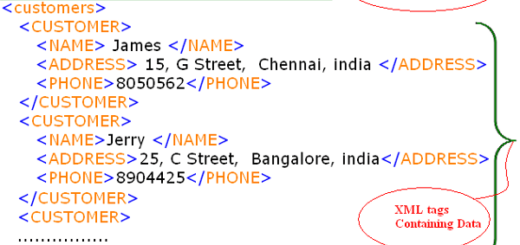
Semantic Information : it explain that XML document builds semantic or meaningful information. Refer to the example of searching name “James Bond”.
-
Other Benefits
Note : XML is a software and hardware independent tool for carrying information. XML is now as important for the Web as HTML was to the foundation of the Web. XML is used in many aspects of web development, often to simplify data storage and sharing.





Recent Comments